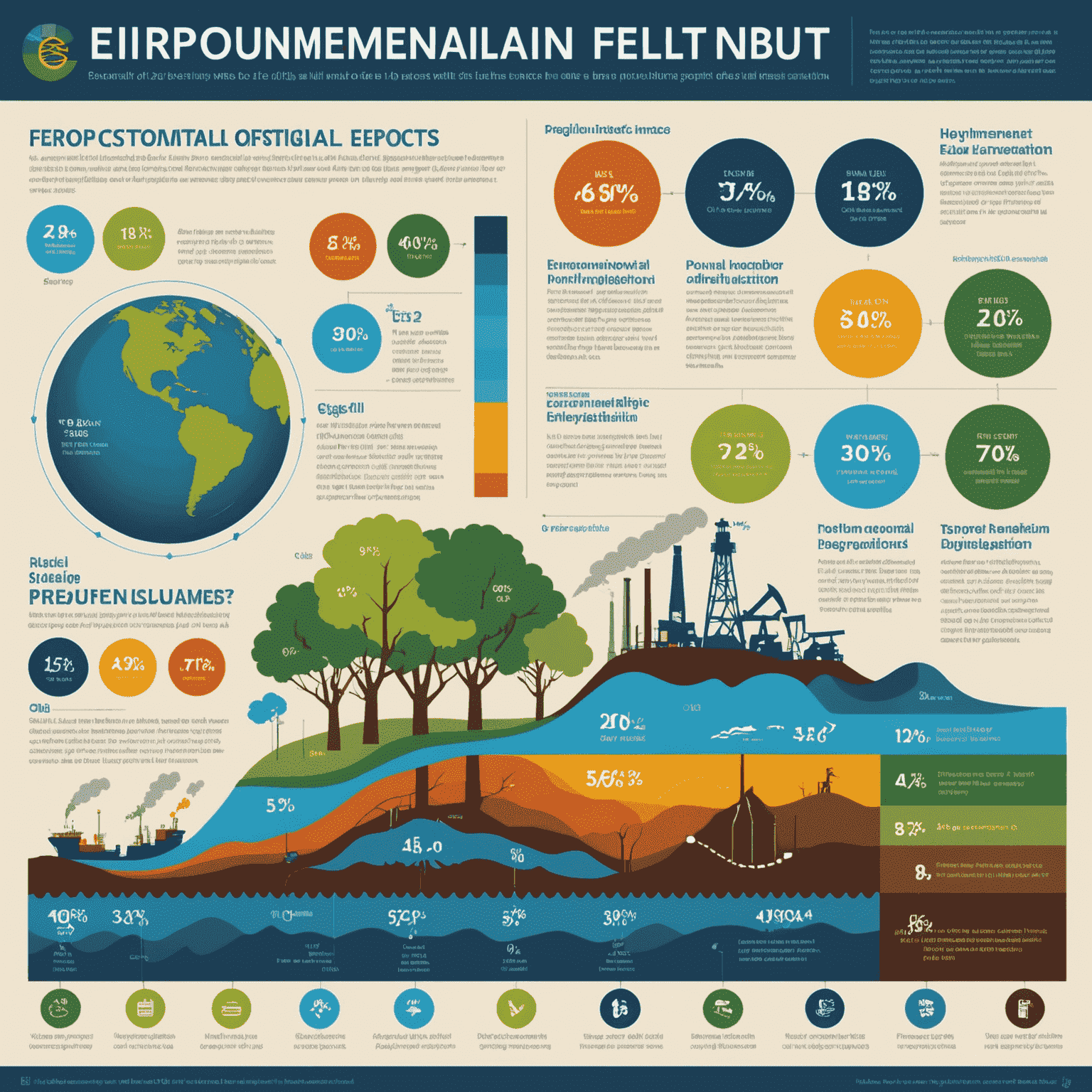
Environmental Challenges in the Oil Sector

The oil sector, while crucial for energy production, faces significant environmental challenges. As the industry has grown from its early days in Canada to become a global powerhouse, so too have concerns about its ecological footprint. This article explores the environmental impacts of oil production and the industry's efforts to address these pressing issues.
Major Environmental Impacts
1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The extraction, refining, and consumption of oil products contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide. These emissions are a primary driver of climate change, affecting global temperatures and weather patterns.
2. Water Pollution
Oil spills and leaks can contaminate both surface and groundwater sources. The chemicals used in extraction processes, such as hydraulic fracturing, also pose risks to water quality if not properly managed.
3. Land Degradation
Oil exploration and production can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction. The construction of infrastructure like pipelines and roads further fragments ecosystems.
4. Air Pollution
The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants during oil production and refining contributes to poor air quality, which can have serious health implications for nearby communities.
Industry Efforts to Address Environmental Concerns
The Canadian petroleum industry, recognizing the need for sustainable practices, has been implementing various measures to mitigate its environmental impact:
- Technological Innovations: Development of cleaner extraction methods and more efficient refining processes to reduce emissions and waste.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Implementation of CCS technologies to capture and sequester carbon dioxide emissions.
- Water Management: Improved water recycling and treatment techniques to minimize freshwater usage and reduce the risk of contamination.
- Land Reclamation: Efforts to restore landscapes and ecosystems after oil extraction activities have ceased.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Investing in and incorporating renewable energy sources into oil production operations.
Regulatory Framework
Canada has implemented stringent environmental regulations for the oil sector, including:
- The Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA)
- The Oil and Gas Operations Act
- Provincial regulations specific to major oil-producing regions like Alberta and Saskatchewan
These regulations set standards for emissions, waste management, and environmental protection, pushing the industry towards more sustainable practices.
Future Outlook
As global pressure mounts to address climate change, the oil sector faces increasing scrutiny and the need for further innovation. The industry's future will likely involve:
- Continued funding in clean technologies
- Greater focus on renewable energy transition
- Enhanced transparency and reporting on environmental impacts
- Collaboration with environmental organizations and indigenous communities
The journey of Canada's energy sector from its early oil discoveries to modern technologies has been marked by significant environmental challenges. As the industry continues to evolve, balancing energy production with environmental stewardship remains a critical priority for ensuring a sustainable future.